end tidal co2 range
Graphically this difference in ROSC vs non-ROSC PetCO2 for both groups appeared to be even greater at ten minutes. 39 Treveno RP Bisera J Weil MH Rackow EC Grundler WG.

Different Capnography Traces A Sudden Drop In E 0 Co2 B Download Scientific Diagram
Total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of the gas Expired CO2 measured PetCO2 mmHg in waveform Percentage Normal Levels PaO2 85-100mmHg PaCO2 35-45mmHg Percentage vs.

. End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath. This prospective cross-sectional study has been carried out over a 3-month. Understanding End Tidal CO 2 Monitoring.
End-tidal CO2 as a guide to successful cardiopulmonary. The normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa.
Norm al EtCO2 levels 46 to 60 kPa signify adequate perfusion. Studies have shown that in patients who had ETCO2 of 10 mmHg or less cardiac arrest was associated with death 13 14. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor.
PetCO2 partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide. It is unclear whether EtCO 2 measured using a portable capnometer is related to PaCO 2 in patients with respiratory diseases. 423 20 mmHg versus 34 255 mmHg.
Et al End tidal Carbon Dioxide Monitoring in very low birth weight infants. Hence CO 2 levels in the expired gas is a parameter that accurately reflects minute ventilation. 2012 Vol 47 4 367-372.
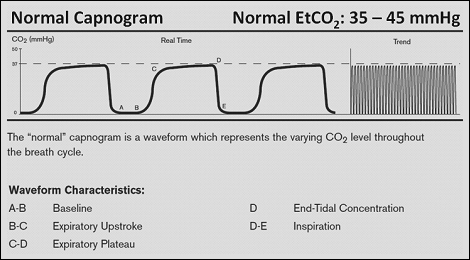
Waveform and end -tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 values. Capnography waveforms etCO2 and breathing patterns Capnography can be used to measure end-tidal CO 2. So the short answer is you are right about the ranges 35-45 but that is for actual PaCo2 drawn from an ABG.
What Should End-tidal Co2 Be Kpa. 428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg. BackgroundPhysiology 2 Monitoring end-tidal CO.
Circulating blood CO 2 is slightly greater than exhaled CO 2 due to a ventilation-perfusion VQ mismatch. Correlation and agreement with arterial carbon dioxide. Takahashi D et al.
Capnography can be used to assess unresponsive patients ranging from those are actively seizing to victims of chemical terrorism. End-tidal carbon dioxide concentration during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. When CO2 diffuses out of the lungs into the exhaled air a device called a capnometer.
MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST Presentation for MSBI Nurses Prepared by Dr. Once that has been done you can use an end tidal Co2 monitor as opposed to drawing multiple ABGs. Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law.
After 20 minutes of CPR death occurs if ETCO2 is consistently below 10 mmHg with 100 sensitivity and specificity 15. At the end of expiration gas sampled from the trachea should be alveolar gas and the CO 2 level will equate to the alveolar and therefore arterial CO2 in dogs and cats that dont have lung disease. In patients with normal pulmonary function CO 2 normally 35 to 45 mm Hg and ETco 2 should correlate closely with a deviation of about 2 to 5 mm Hg.
A number of factors such as tachypnea ventilation-perfusion inequality and airway dead space are described to influence differences between end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 and PaCO 2. Normal range No measure of cardiac performance 1. Cross-sectional associations between ETCO2 and PaCO2 were examined in the study.
According to the book by Hockenberry and Wilson 2015 p 1140 normal values of ETCO2 are 30-43 mmHg which is slightly lower than arterial PaCO2 35-45mmHg. This type of capnometry identified 91 of the instances when the arterial CO2 pressure was between 34 and 54 mm Hg using an end-tidal range of 29 to 45 mm Hg. The relationship between EtCO 2 and PaCO 2 was poor in.
MmHg Relate to the air we breath. Understanding End Tidal CO 2 Monitoring. ETCO2 is a reliable indicator with a high prognostic value in determining the CPR outcome 11 12.
In mmHg the PetCO2 values for those with and without ROSC after five minutes of CPR was. The protocol prescribed to maintain ET co2 between 35 and 45 mmHg and to keep the systolic blood pressure SBP less than 180 mmHg before treatment and less than 220 mmHg after securing the aneurysm while maintaining a MAP greater than 80 mmHg. Effect of tidal volume and end tracheal tube leakage on.
Within an acceptable range. 78 Nitrogen 21 Oxygen 1 CO2 and other gases Exhaled gases. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHg.
It is best to get an ABG along side the end tidal to calculate the patients shunt. End-tidal carbon dioxide and els may have been underestimated3435 outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. An important use of continuous ETCO 2.
In conditions of normal breathing 6 Lmin 12 breathsmin 500 ml for tidal volume etCO 2 is very close to alveolar CO2. The presence of a normal waveform denotes a patent airway and spontaneous breathing. The normal values are 5-6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as. As stated before end tidal is slightly different. End Tidal CO 2 sampling Ventilatory function minute ventilation decreases and therefore CO2 increases in a A dead space gasno CO2 B mixed.
The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory. After 20 minutes of CPR death occurs if ETCO2 is consistently below 10 mmHg with 100 sensitivity and specificity 15. End-tidal values outside this range had a 63 accuracy in predicting hypocarbia or hypercarbia.
Pierre Kory Laura OBrien RN CNS. In infants and children breathing spontaneously the PETCO 2 values range from 36-40 mmHg9 Normally PETCO 2. We aimed to determine the value of sidestream end-tidal carbon dioxide SS-ETCO2 measurement in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD in the emergency department.
N Engl J Med 1988318607-11. NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as ROSC. End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide.

Pdf Capnography In Pediatric Critical Care Unit And Correlation Of End Tidal And Arterial Carbon Dioxide In Ventilated Children

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

Basic Waveform Capnography As A Continuous Monitoring Tool During Mechanical Ventilation

Exhaled Carbon Monoxide End Tidal Co2 And Peripheral Oxygen Saturation Download Table

Exhaled Carbon Monoxide End Tidal Co2 And Peripheral Oxygen Saturation Download Table
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Capnogram R Series Defibrillator Zoll Medical Uk

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Recording Of Ventilated Children In Picu N 535 Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Pdf Applications Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Monitoring In Emergency Department A Narrative Review Semantic Scholar

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
